OS/Linux
-
[CentOS] CentOS 7 - Redis 설치 위치 및 버전 확인2021.11.01
-
[CentOS] Linux Service 등록하는 방법2020.12.02
-
[CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기2020.03.06
-
[CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd2020.02.25
[Linux] 리눅스 종류 및 버전 확인하는 방법 - CentOS, Ubuntu
| 들어가며 |
Linux는 버전에 대한 영향을 받는 OS 이다 보니, 이전에 설치한 버전을 확인해야 하는 경우가 빈번히 발생을 하는데요. 이때 알아두면 좋을 명령어 및 방법을 정리하였습니다.
01. uname -a
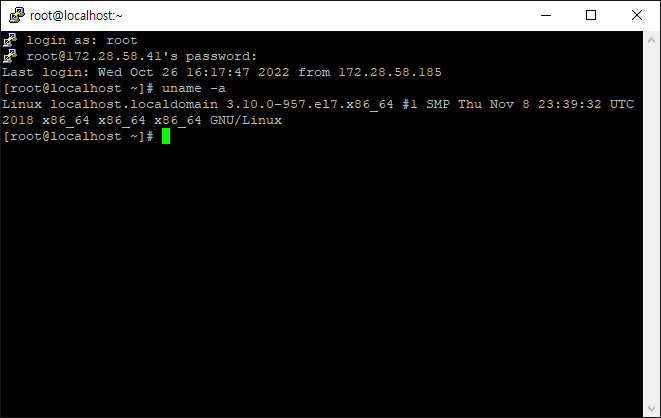
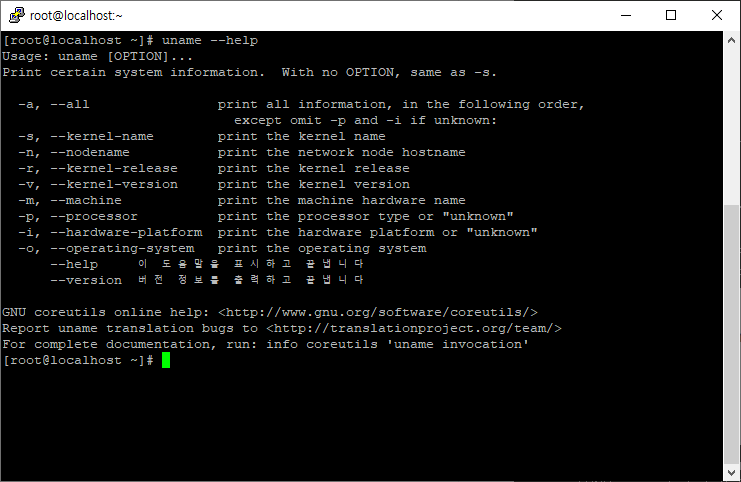
$ uname -a 옵션의 경우 모든 정보를 출력하는데요. --help 옵션으로 확인시 -a 옵션을 제외한 내용들이 순차적으로 출력이 됩니다.
Linux localhost.localdomain 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Thu Nov 8 23:39:32 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
커널이름 -s : Linux
호스트이름 -n : localhost.localdomain
커널릴리즈 -r : 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64
커널 버전 -v : #1 SMP Thu Nov 8 23:39:32 UTC 2018
하드웨어 -m : x86_64
프로세스 타입 -p : x86_64
하드웨어 플랫폼 -i : x86_64
운영체제 -o : x86_64 GNU/Linux
의 순서로 출력이 됩니다.
02. os-release 파일을 이용한 버전확인
다음은 os-release 파일을 이용해서도 버전 정보를 확인 할 수 있는데요.
아래 두가지 명령어로 확인이 가능합니다.
$ cat /etc/os-release
$ grep . /etc/os-release
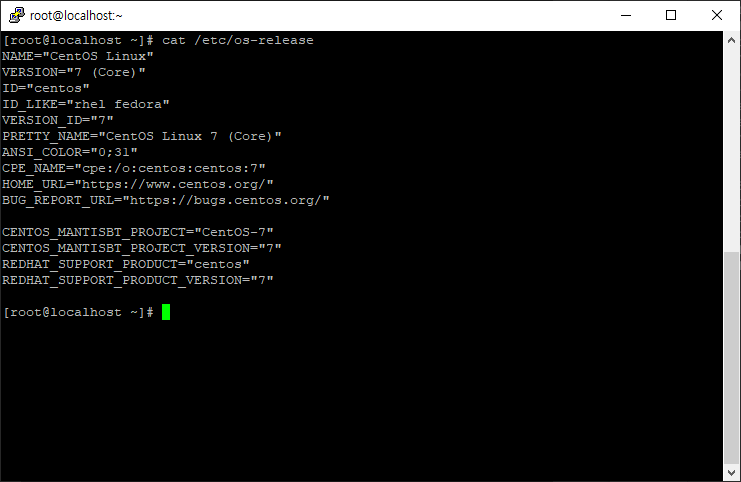


03. hostnamectl 을 이용한 버전확인
hostnamectl 명령어를 이용해서도 버전을 확인할 수 있습니다.
hostnamectl 명령어는 호스트에 대한 정보 및 호스트 이름을 변경할 때 사용하는 명령어 인데요.
상태를 확인 할때도 사용하게 됩니다.
$ hostnamectl status
status 옵션은 생략가능한 기본 옵션이여서, 호스트 정보를 확인 할 때 사용도 되지만, OS 및 버전정보도 같이 보여주기 때문에 해당명령어를 이용해서도 버전정보를 확인 가능합니다.
04. lsb_release -a
lsb_release 명령어는 리눅스의 배포판 버전을 확인하는 명령어 입니다.
아래와 같은 명령어로 확인이 가능합니다.
$ lsb_release -a

05. lsb_release 가 설치 안되 있을 경우.
간혼, lsb_release 명령어가 설치가 안되어 있을 경우가 있습니다. 해당 명령어를 입력할 경우 아래와 같이 명령어를 찾을 수 없다는 메시지가 출력되는 경우인데요.

해당 경우 yum 명령어를 이용해서 lsb 를 설치해주시면 됩니다.
$ yum install redhat-lsb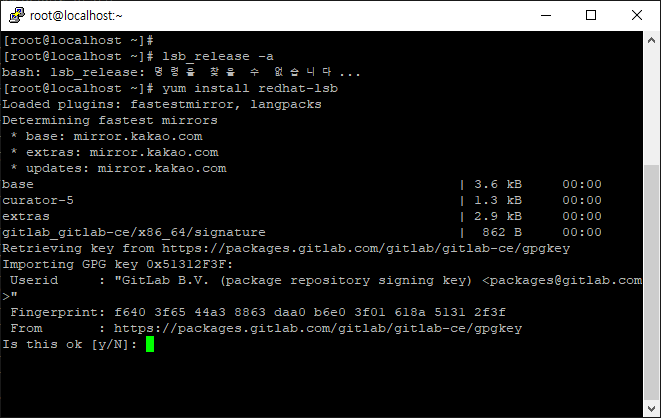


| 참조 |
https://rhrhth23.tistory.com/145
END
'OS > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CentOS] CentOS 7 - Redis 설치 위치 및 버전 확인 (0) | 2021.11.01 |
|---|---|
| [CentOS] Linux Service 등록하는 방법 (0) | 2020.12.02 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기 (0) | 2020.03.06 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 - NGINX 설치 방법 (4) | 2020.03.02 |
| [CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd (0) | 2020.02.25 |
[CentOS] CentOS 7 - Redis 설치 위치 및 버전 확인
한번 설치하게 되면, 계속해서 사용하고 있기 때문에, 간혹 Redis의 설치 위치를 까먹는 경우가 있어서
기본적인 위치만 정리해서 남겨놓으려고 합니다.
서비스파일은
/etc/init.d경로에 위치하고 있으며, 기본적으로 설치하셨다면 redis_6379 파일에 기본적인 서비스 정보가 기입되어 있습니다.
해당 경로에 있는 redis_6379 파일을 vim 명령어로 열어보면, 기본적으로 어떤 구성으로 되어 있는지 확인 할 수 있습니다.
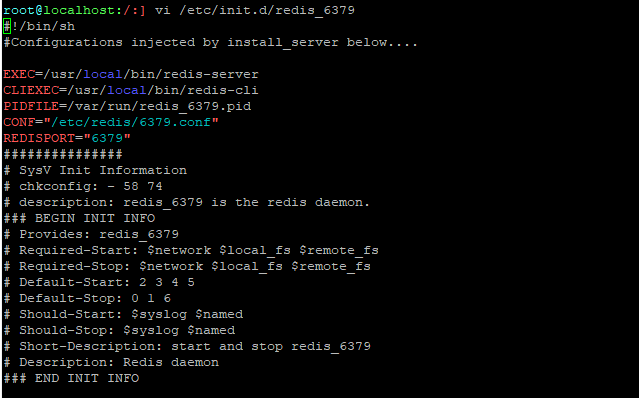
아래 내용은 생략하고,
서버 : /usr/local/bin/redis-server
클라이언트 : /usr/local/bin/redis-cli
등등 기본적인 파일 위치를 확인 할 수 있습니다.
버전확인
root@localhost:/:] /usr/local/bin/redis-cli --version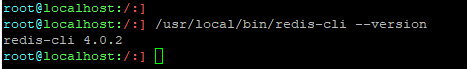
'OS > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Linux] 리눅스 종류 및 버전 확인하는 방법 - CentOS, Ubuntu (1) | 2023.12.11 |
|---|---|
| [CentOS] Linux Service 등록하는 방법 (0) | 2020.12.02 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기 (0) | 2020.03.06 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 - NGINX 설치 방법 (4) | 2020.03.02 |
| [CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd (0) | 2020.02.25 |
[CentOS] Linux Service 등록하는 방법
CentOS 7부터는 이전에 사용하던 SysV(init system) 대신하여, systemd 을 system & service manager 로 사용합니다.
systemctl는 systemd 를 컨트롤하는 cli 명령어입니다.
1. Service 등록
[root@ ] #cd /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants먼저 위의 경로로 이동해 줍니다.
CentOS6 까지는 /etc/rc.d/init.d 디렉토리에 서비스 관련 파일들이 있었습니다.
CentOS7부터는 서비스들이 대부분 Unit으로 분리되었고, 이 Unit들은 [서비스이름].service 파일명으로 생성하며, systemctl 명령어로 제어하도록 변경되었습니다.
아래와 같이 testserver.service 이름의 파일을 생성해 줍니다.
[root@ ] #vi testserver.service[Unit]
Description=Test Server
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/share/dotnet/dotnet /opt/test-server/TestServer/TestServer.dll
WorkingDirectory=/opt/test-server/TestServer
KillSignal=SIGINT
SyslogIdentifier=testserver
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
WorkingDirectory 가 다를 경우, 각 프로그램에서 제아하는 폴더의 경로 때문에, 파일 생성 및 읽기가 비정상적으로 동작할 수 있습니다.
dotnet 으로 구성한 서버였는데, BaseDirectory를 가져오는 부분이 WorkingDirectory 로 인해 잘못 Load 하는 경우가 있었습니다.
2. 서비스 시작
[root@ ] #systemctl stop testserver.service
[root@ ] #systemctl start testserver.service
[root@ ] #systemctl enable testserver.service
[root@ ] #systemctl disable testserver.service등록을 마쳤다면, 위와 같이 systemctl 명령어를 이용해서 service를 제어할 수 있습니다.
출처
'OS > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Linux] 리눅스 종류 및 버전 확인하는 방법 - CentOS, Ubuntu (1) | 2023.12.11 |
|---|---|
| [CentOS] CentOS 7 - Redis 설치 위치 및 버전 확인 (0) | 2021.11.01 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기 (0) | 2020.03.06 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 - NGINX 설치 방법 (4) | 2020.03.02 |
| [CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd (0) | 2020.02.25 |
[CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기
FTP 서버 구축 순서
1. vsftpd 패키지설치
2. 서버 설정 (conf 파일 및 허용리스트 작성)
3. 방화벽 설정 & selinux해제
4. 데몬재시작
5. 추가사항
6. 재시작 에러시 대처
1. vsftpd 패키지 설치
grep 명령어를 이용해서 vsftpd 가 설치 되어 있는지 확인 합니다.
[root@localhost /]# ps -ax | grep vsftpd
79682 pts/2 R+ 0:00 grep --color=auto vsftpd
이후 yum 명령어를 이용해서 vsftpd 패키지를 설치 합니다.
[root@localhost /]# yum -y install vsftpd
2. 서버설정
conf 파일을 이용해서, ftp 관련한 설정을 해줍니다. 해당 경로는 아래를 참고해주세요.
[root@localhost etc]# vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
[root@localhost etc]#
해당 conf 파일에서 저는 아래 3개의 설정을 변경했습니다.
익명 허용 여부와, 허용 리스트를 관리해주는 부분입니다.
anonymous_enable=YES
chroot_list_enable=YES
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
ESC 키를 누르고 :set nu 를 입력하면, 아래와 같이 줄 수가 표시됩니다.


허용리스트 파일을 아래와 같이 conf 파일에 설정 해 주었기 때문에, 해당 경로에 허용할 아이디 리스트를 입력하여 줍니다.
chroot_listchroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
[root@localhost etc]# vi /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
[root@localhost etc]#
3. 방화벽 설정
기본적으로 FTP는 21번 포트를 사용합니다. 리눅스의 경우 웬만한 방화벽은 막혀 있다고 보시면 됩니다.
그래서 firewall-cmd 명령어를 이용해서 방화벽을 해제해 줍니다.
저는 그냥 21번 기본 포트를 사용하였으며, 원하시는 포트로 변경해도 됩니다.
[root@localhost etc]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ftp
success
[root@localhost etc]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=21/tcp
success
[root@localhost etc]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@localhost etc]#
SELINUX 해제
SELinux 는 Linux의 보안을 강화해 주는 보안 강화 커널이고 zero-day 공격 및 buffer overflow 등 어플리케이션 취약점으로 인한 해킹을 방지해 주는 핵심 구성요소입니다.
SELinux 는 저도 공부가 더필요한 영역이라, 자세한 설정은 여기서 다루지 않겠습니다.
일단 SELINUX를 해제하는 방식으로 보안의 영역을 최소화 하겠습니다.
[root@localhost etc]# vi /etc/selinux/config# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
SELINUX=enforcing 을 disabled로 변경하여 준다.
4. 데몬 재시작
[root@localhost etc]# systemctl enable vsftpd
[root@localhost etc]# systemctl restart vsftpd
5. 추가 사항
간혹 root 계정을 이용해서 FTP 에 접속하는 경우 503 에러를 발생하는 경우가 있는데요. 이는 root 계정이 접속 거부 리스트에 등록되어 있는 경우 입니다.
root 거부리스트 계정 제거
아래 각각 명령어를 이용해서 보여지는 리스트에서 root 계정을 제거해 줍니다.
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/vsftpd/user_list
# Users that are not allowed to login via ftp
root -> 제거
bin
daemon
adm
lp
sync
shutdown
halt
mail
news
uucp
operator
games
nobody
6. 재시작 에러시 대처
재시작할 경우 아래와 같은 오류가 발생하는 경우가 있습니다.
이는 IPv4 / IPv6 와 관련된 에러내용이며, 둘다 YES 로 되어 있는 경우 발생하는 오류입니다.
vsftpd.conf 파일을 이용해서 listen=YES, listen_ipv6=YES 두 영역을 찾아서 하나를 NO로 변경해줍니다.
보통 IPv6를 사용안하시기 때문에, 저의 경우 listen_ipv6를 NO 로 변경하였습니다.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start vsftpd
Job for vsftpd.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status vsftpd.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status vsftpd.service
● vsftpd.service - Vsftpd ftp daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since 화 2020-02-25 14:20:28 KST; 12s ago
Process: 1475 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf (code=exited, status=2)
2월 25 14:20:28 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting Vsftpd ftp daemon...
2월 25 14:20:28 localhost.localdomain vsftpd[1475]: 500 OOPS: can only support ipv4 and ipv6 currently
2월 25 14:20:28 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: vsftpd.service: control process exited, code=exited status=2
2월 25 14:20:28 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Failed to start Vsftpd ftp daemon.
2월 25 14:20:28 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Unit vsftpd.service entered failed state.
2월 25 14:20:28 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: vsftpd.service failed.
112 # When "listen" directive is enabled, vsftpd runs in standalone mode and
113 # listens on IPv4 sockets. This directive cannot be used in conjunction
114 # with the listen_ipv6 directive.
115 listen=YES
116 #
117 # This directive enables listening on IPv6 sockets. By default, listening
118 # on the IPv6 "any" address (::) will accept connections from both IPv6
119 # and IPv4 clients. It is not necessary to listen on *both* IPv4 and IPv6
120 # sockets. If you want that (perhaps because you want to listen on specific
121 # addresses) then you must run two copies of vsftpd with two configuration
122 # files.
123 # Make sure, that one of the listen options is commented !!
124 listen_ipv6=NO
'OS > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CentOS] CentOS 7 - Redis 설치 위치 및 버전 확인 (0) | 2021.11.01 |
|---|---|
| [CentOS] Linux Service 등록하는 방법 (0) | 2020.12.02 |
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 - NGINX 설치 방법 (4) | 2020.03.02 |
| [CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd (0) | 2020.02.25 |
| [Linux] CentOS, Ubuntu 등 OS 버전을 확인하는 명령어 (0) | 2020.02.08 |
[CentOS 7] CentOS 7 - NGINX 설치 방법
CentOS 7 버전에 Nginx 설치 방법 정리
요약
- yum 외부 저장소 추가
- yum install
- 방화벽 포트 개방
- nginx 포트 설정
- nginx 데몬 실행
- 실행
1. yum 외부 저장소 추가
yum 저장소에는 nginx가 없기 때문에 외부 저장소를 추가 해야 하며,
[root@localhost /]# cd etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Sources.repo CentOS-Vault.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo microsoft-prod.repo
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# vi nginx.repo
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]#
/etc/yum.repos.d/ 경로에 nginx.repo 파일을 추가하고 아래와 같이 작성해줍니다.
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
위 내용은 공식 사이트에 있으며, OS가 다르다면 해당 OS에 맞게 수정해 주면 됩니다.
2. yum install
yum install 명령어를 이용해서 설치해 줍니다.
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y nginx
3. 방화벽 포트 개방
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8089/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
21/tcp 5000/tcp 5001/tcp 8089/tcp
[root@localhost ~]#
4. Nginx 포트 설정
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
5. Nginx 데몬 실행
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
6. 실행화면
정상적으로 데몬이 실행되었다면, http://localhost:8080 접속시 아래와 같은 페이지가 보여집니다.

CentOS7 Nginx 설치 방법
CentOS7 에 Nginx 설치 방법에 대해서 설명한다. yum을 활용하여 쉽게 설치해 보자. 요약 yum 외부 저장소 추가 yum install 방화벽 포트 개방 nginx 포트 설정 nginx 데몬 실행 데몬 실행시 오류 발생 (오류 ��
cofs.tistory.com
'OS > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CentOS] Linux Service 등록하는 방법 (0) | 2020.12.02 |
|---|---|
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기 (0) | 2020.03.06 |
| [CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd (0) | 2020.02.25 |
| [Linux] CentOS, Ubuntu 등 OS 버전을 확인하는 명령어 (0) | 2020.02.08 |
| [CentOS 7] Network 관련 셋팅 명령어 정리 (0) | 2019.12.10 |
[CentOS 7] 방화벽 해제하기 - firewall-cmd
윈도우 기반의 서버에서만 작업을 하다, 리눅스 환경에도 적응하기 위해 노력중입니다. MS의 정책도 멀티 플랫폼 기반으로 지속적으로 변경을 요하기 때문에 시대에 맞춰, 윈도우 뿐만 아니라 리눅스 환경도 지속적인 공부가 필요해 보입니다. 리눅스 환경을 셋팅하면서 간혹 잊어버리는 부분을 지속적으로 정리해 봅니다.
1. 방화벽 포트 등록
[root@localhost /]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
2. 방화벽 서비스 해제
[root@localhost /]# systemctl stop firewalld
3. 재부팅시 방화벽 실행하지 않기
[root@localhost /]# systemctl disable firewalld
4. 방화벽에 등록된 포트 리스트 가져오기
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
21/tcp 5000/tcp 5001/tcp 8089/tcp
'OS > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 FTP 설치 및 설정하기 (0) | 2020.03.06 |
|---|---|
| [CentOS 7] CentOS 7 - NGINX 설치 방법 (4) | 2020.03.02 |
| [Linux] CentOS, Ubuntu 등 OS 버전을 확인하는 명령어 (0) | 2020.02.08 |
| [CentOS 7] Network 관련 셋팅 명령어 정리 (0) | 2019.12.10 |
| [CentOS 7] 리눅스 디렉토리 구조 (1) | 2019.12.10 |